Arthritis is a complex family of joint disorders that involves inflammation of one or more joints. It consists over 100 different diseases that destroy joints, bones, muscles and other connective tissues by hampering physical movement. Basically, arthritis is regarded as the disease of the elder ones, but children can also be affected by the same. An estimated, 70% individuals above the age of 65 in North America are affected by arthritis. This disease is common among women as compared to men and affects all races, groups and cultures.
Types of arthritis:
There are various forms of arthritis in which joint pain is primary, these are described below:
 Osteoarthritis- It is also known as degenerative arthritis, a group of mechanical abnormalities, which involves degradation of joints. Joint pains, tenderness and stiffness are some of the symptoms of Osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis- It is also known as degenerative arthritis, a group of mechanical abnormalities, which involves degradation of joints. Joint pains, tenderness and stiffness are some of the symptoms of Osteoarthritis.- Gout and pseudo-gout- Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease, known as pseudogout, is a rheumatologic disorder. Its symptoms arise from the accumulation of crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate in the connective tissues. In this disorder, the knee joint is the most commonly affected part of the body.
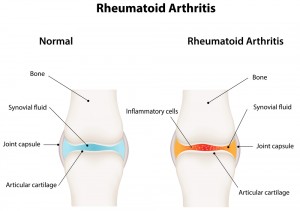
- Rheumatoid arthritis– This form of arthritis is an autoimmune disease that results in a chronic and systemic inflammatory disorder affecting various body tissues and organs. Rheumatoid arthritis is a painful condition, which may lead to substantial loss of functioning if not treated accurately.
- Juvenile arthritis- This disease is also known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and is most common in children and adolescents (below the age of 16 years). Juvenile arthritis commonly occurs in children between the ages of 7 to 12. Reduced physical activity and poor appetite are the main symptoms of juvenile arthritis.
Explaining rheumatoid arthritis:
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder, which affects small joints in the hands and feet. In some people this chronic disease leads to the inflammation and destruction of the bone, and ligaments, causing deformity of the joints. Rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of joints and causes a painful swelling that may result in bone erosion and joint deformity.
Research is still going on that what starts rheumatoid arthritis, but the causes are still not known completely. Doctors believe that genetic components and environmental factors appear likely. Certain genes have been identified that increase the risk for rheumatoid arthritis. It has been proved in a study that genes don’t actually cause rheumatoid arthritis, but they can make the person more susceptible to environmental factors such as smoking, exposure to silica, and chronic periodontal disease all increase the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Initially, rheumatoid arthritis affects the smaller joints that attach your fingers to hands and your toes to feet. As the progression of the disease, symptoms spread to the knees, ankles, elbows, hips and shoulders. Signs and symptoms of rheumatoid include:
- Tender, warm, and swollen joints
- Fatigue, fever and weight loss
- Morning stiffness
- Bumps of tissue under the skin on your arms
After analyzing and monitoring the symptoms, now the time has come to prepare for an appointment with your doctor, and then he will perform rigorous blood tests and X-rays to diagnose the exact situation of rheumatoid arthritis. After confirming the disease, he will start your treatment whether it is through medications or therapies.
It has been proved in science that there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis. But, the goal of treatment is generally to reduce joint inflammation and pain, and maximizing the joint function by preventing joint destruction and deformity. Various medications are provided by doctors with fewest side effects such as steroids and immunosuppressant, which provide relief to the patients by reducing their pain and stiffness.
Therapies are another treatment options in which your doctor may send you to an expert who will perform therapy or teach you exercises, which will definitely help you in keeping your joints flexible.
Detailing juvenile arthritis:
Juvenile arthritis (JA) is a disease with autoimmune and inflammatory conditions that develops in children ages 16 and younger. An estimated, 294,000 children and teens suffer from juvenile arthritis in the U.S. This disease is said to be the most common among children in the United States. Juvenile arthritis is also idiopathic, which means that there is no exact cause known. Moreover, researchers believe that juvenile arthritis may be caused due to genetics, certain infections, and environmental triggers. There are various types of juvenile arthritis, these are:
- Systemic arthritis- This type of juvenile arthritis is known as Still’s disease, which affects the entire body or involves many systems of the body. High fever and rashes are the main signs of systemic arthritis. Additionally, systemic juvenile arthritis affects internal organs like the heart, liver, spleen, and lymph nodes, but not the eyes.
- Oligoarthritis– This type is known as pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis that affects the joints of the child. Oligoarthritis affects the eye, most often the iris and is more common among girls than boys.
- Psoriatic arthritis- This juvenile arthritis type affects the children with arthritis and skin disorder called psoriasis. In this type, the child often has pitted fingernails.
- Enthesitis– This arthritis often affects the spine, hips and eyes. Boys older than 8 years of age are at high risk of getting attacked by enthesitis.
There are various symptoms that affect every disease as in the case of juvenile arthritis. In this, children may produce no symptoms at all, but symptoms may only vary depending on the type of arthritis. Some of the symptoms of juvenile arthritis may include joint stiffness, especially in the morning, limping, persistent fever, rash, weight loss, pain, swelling, and tenderness in the joints, fatigue, eye redness and blurred vision.
Diagnosis of juvenile arthritis is difficult because a child may have no symptoms. Basically, there is no actual test for juvenile arthritis and the diagnosis of it only happens by excluding other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
After diagnosis of JA, the best approach to treat a child includes medical professionals such as occupational therapist (OT), physical therapist and nurse. Each and every medication and therapy is beneficial for the child. Drugs and medications only provide relief from pain but cannot eradicate the problem. Some of the procedures of treatment are as follows:
- Physiotherapy and occupational therapy is very important to prevent the deformities of juvenile arthritis.
- Children with JA are advised to participate in as much physical activity as possible.
- Steroids are a part of medications prescribed for those experiencing moderate to severe juvenile arthritis consequences. These medications may be administered orally or injected directly into an involved joint.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed by the doctors used to treat pain and swelling only. Nausea and stomach ache are some of the side effects that children may face after consuming the above mentioned drugs.
- Autologous stem cell transplantation is the last treatment option and is for those children suffering from juvenile arthritis who have failed all of the above therapeutic and medical options. This procedure requires hospitalization and the treatment is done in two-step process. In the initial portion, high-dose immune suppression medications are provided to remove the patient’s lymphocytes which are attacking the patient’s joint. After removal, new stem cells of the patient, which were previously harvested, stored, or treated, are introduced back into the patient’s body via the bloodstream.
Also Read here, the different ways of preventing heart attack and stroke: Heart Attack- Know the risk
Now that you know of the causes and physiotherapy treatments, you can share this article with adults or teenagers who are suffering from arthritis. You can also post questions if you have any in the comment boxes.