Antifungal creams play a crucial role in controlling fungal infections, relieving symptoms, and preventing complications. This article helps you learn about antifungal cream use and how they help manage fungal conditions.
Understanding topical antifungals
Fungal diseases have become a major medical concern. It is tough to manage because they tend to be chronic and hard to diagnose. Fungal infections are common, affecting individuals of almost all ages, and can develop on various parts of the body, such as the skin, scalp, nails, groin, and skin folds.
What are antifungal creams used for? Antifungal creams are topical medications specifically formulated to treat various skin fungal infections. These preparations contain active ingredients that stop fungal growth, either by killing the fungus or by preventing its reproduction.
How and when to use antifungal cream?
An antifungal cream is applied to the skin, where it penetrates and targets the infection, reducing symptoms such as redness, itching, and inflammation. They work by breaking down the fungi’s cell membranes, preventing them from growing and spreading. Antifungal creams target specific components of fungal cells, helping treat common skin conditions like ringworm, athlete’s foot, and yeast infections, restoring your skin’s health and much-needed comfort. Commonly used antifungal creams include miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine, ketoconazole and econazole.
Antifungal cream use in bief
Management of athlete’s foot – Also known as tinea pedis, this fungal infection affects a significant number of people worldwide. The condition may present as asymptomatic, mild, or severe itchiness, pain, trouble walking, and other debilitating symptoms. It is a contagious fungal infection that causes itchy feet. The fungal infection appears as an itchy, stinging, burning sensation on the infected skin. It is common between your toes, but it can also appear on the tops of your feet, the soles of your feet and your heels. The infected skin may appear scaly and cracked or develop blisters. Appropriate treatment can stop the fungus from spreading and clear it up. Numerous preventive measures are available, and topical antifungals can be an effective option for treating athlete’s foot. Prescription antifungal creams such as clotrimazole, tolnaftate, miconazole or terbinafine effectively treat athlete’s foot.
Treatment of ringworm – You might not even realise that it’s not a worm but a fungus that causes ringworm. Skin ringworm can spread easily through close contact. These infections are usually treated with antifungal creams, which are applied to the skin for about 2 to 4 weeks. They work best when applied for the full duration as directed, even if symptoms begin to improve. Ringworm is an itchy, contagious skin condition that can develop into a ring-shaped pattern. Topical antifungals can stop the fungus from spreading to other parts of yoru body or to other individuals. Antifungal agents such as clotrimazole, terbinafine, miconazole, and ketoconazole are available to treat ringworm.
Treatment of jock itch – Very similar to ringworm, Jock Itch is a common fungal infection. It causes an itchy, burning, stinging rash around the groin, inner thighs and butt crack. Jock itch, also called tinea cruris, is a fungal infection. Patients with this infection may find that their skin becomes scaly and cracked, or that they develop bumps or blisters. The infected skin may appear red, grey, purple, or white. If left untreated, it can spread to other areas of your body, including your nails, hands, and feet. Using an antifungal cream is the fastest way to cure jock itch. Topical antifungals such as miconazole, clotrimazole, terbinafine or tolnaftate.
Control of yeast infection on the skin – Yeast infections are a common medical annoyance. But most can be managed with healthy habits and antifungal formulations. The antifungal formulations are effective in treating yeast infections in skin folds, around the navel, under the breasts, or in diaper areas in babies. Topical antifungal formulations help restore skin health and reduce symptoms such as soreness, itching, and redness.
Calms down the surrounding area of the nail – Although topical antifungals are not enough to treat deep nail infections, they can help treat fungal infections around the nails. The surrounding skin often appears itchy, inflamed, and scaly. Applying antifungal creams in such cases can significantly reduce fungal growth, relieve discomfort, and improve overall nail health when combined with appropriate hygiene and nail care practices.
Treatment of facial fungal infections – Certain antifungal creams are formulated for use on the face. The affected facial skin areas may appear red, scaly, or itchy, or may show patchy hair loss. Antifungal preparations, when used as directed, can help control fungal growth in sensitive areas of the face, such as the hairline, eyebrows, and beard. They are often recommended along with medicated shampoos for the best results.
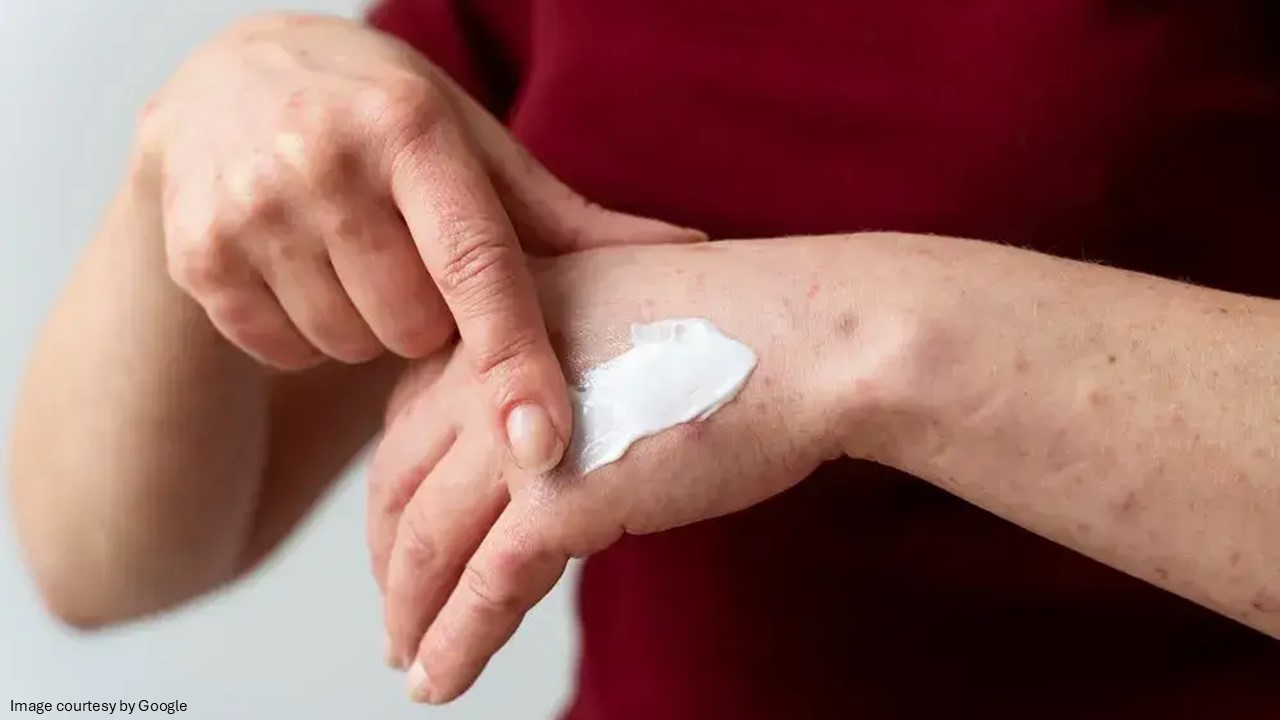
Prevention of secondary skin infections
Antifungal creams can sometimes be prescribed as preventive treatment for individuals prone to recurrent fungal infections. People with diabetes, athletes, and those with weakened immune systems may benefit from occasional preventive use in high-risk areas. Early control of fungal growth helps reduce the risk of secondary bacterial infections that can occur when the skin is damaged or inflamed.
Use appropriately for optimal results
For antifungal formulations to be effective, you must use them correctly.
How to apply antifungal cream: Make sure the affected area is clean and dry before applying the cream. Squeeze out a little to cover the affected area. Gently rub the formulation into your skin, then wash your hands afterwards.
How long to use antifungal cream: A thin layer must generally be applied 1 to 2 times for about 2 to 4 weeks. Consistently use the topical antifungal and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms have improved. Stopping the topical treatment too early may allow the fungus to recur. Avoid sharing personal skin care items, such as towels and clothing, throughout the treatment to prevent infection.
Conclusion
Antifungal creams are effective in managing a wide range of fungal infections. From treating common skin conditions like athlete’s foot and ringworm to preventive therapy for more complex skin issues, their uses are valuable. When used appropriately, antifungal creams can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent the spread of infection. They are widely available worldwide. Their accessibility and effectiveness make them essential to skincare and personal health management.




